Speed Symbol indicates the maximum speed at which the weight (with the exception of weight when speed
is equal to or exceeds 210 km/h) designated by the manufacturing company can be supported by the tire.

What is my tire’s maximum speed?
Enter your tire’s Speed Symbol in the blank and click the “Enter” key!
Speed symbol value (possible input range: A1~Z) = km/h
Speed according to speed symbol
1km per hour(km/h)= 0.621371mi/h
Speed Symbol indicates the maximum speed at which the weight (with the exception of weight when speed
is equal to or exceeds 210 km/h) designated by the manufacturing company can be supported by the tire.
| Speed rating | |||||
| Code | km/h | mph | Code | km/h | mph |
| A1 | 5 | 3 | L | 120 | 75 |
| A2 | 10 | 6 | M | 130 | 81 |
| A3 | 15 | 9 | N | 140 | 87 |
| A4 | 20 | 12 | P | 150 | 94 |
| A5 | 25 | 16 | Q | 160 | 100 |
| A6 | 30 | 19 | R | 170 | 106 |
| A7 | 35 | 22 | S | 180 | 112 |
| A8 | 40 | 25 | T | 190 | 118 |
| B | 50 | 31 | U | 200 | 124 |
| C | 60 | 37 | H | 210 | 130 |
| D | 65 | 40 | V | 240 | 149 |
| E | 70 | 43 | Z | over 240 | over 149 |
| F | 80 | 50 | W | 270 | 168 |
| G | 90 | 56 | (W) | over 270 | over 168 |
| J | 100 | 62 | Y | 300 | 186 |
| K | 110 | 68 | (Y) | over 300 | over 186 |
Load index shows in codified form the maximum weight that can be supported by one tire while driving.
For example, if the load index is 100, it means that a tire can support a maximum of 800kg.

How much weight can your tire support?
Enter your tire’s Load Index in the blank and click the “Enter” key!
Load Index value (possible input range: 0~279) =
Weight According to Load Index
kg(kilogram) = 1pound(lb) = 0.4536kg
Tire Section Width
The distance in a straight line between the sidewalls when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Tire Section Height
The result of subtracting rim diameter from the tire’s outer diameter and dividing by 2
Rim Diameter
The distance between the rim bases in contact with the rim flange (almost identical to the tire’s interior diameter).
Tire Overall Diameter
Tire interval when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Tire Section Width
The distance in a straight line between the sidewalls when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Tire Section Height
The result of subtracting rim diameter from the tire’s outer diameter and dividing by 2.
Tire Overall Diameter
Tire interval when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Rim Diameter
The distance between the rim bases in contact with the rim flange (almost identical to the tire’s interior diameter).
Click the buttons for terminology and meanings of various parts of a passenger tire!

Tire Section Width
The distance in a straight line between the sidewalls when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Tire Section Height
The result of subtracting rim diameter from the tire’s outer diameter and dividing by 2
Tire Overall Diameter
Tire interval when the tire is attached to the rim, air pressure has been matched to tire standards and no weight is on the tire.
Rim Diameter
The distance between the rim bases in contact with the rim flange (almost identical to the tire’s interior diameter).
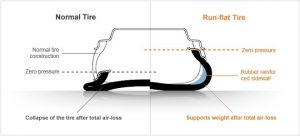
The Run-flat tire allows a car to travel at a speed of up to 80 kmp/h, even after losing internal air pressure due to tire damage(i.e. flat tire).
The installation of a TPMS(Tire Pressure Monitoring System) to sense changes in tire pressure is highly recommended to allow drivers to take appropriate measures in emergency situations.
Winter Tire
Winter tires are widely used for passenger cars, light trucks, trucks and buses and are indispensible in regions with heavy snowfall. In general, the treads of winter tires are divided into small blocks to maximize driving performance in snow with the added traction capability of rug tread and the anti-side slip capability of rib tread.
Winter tires are made of a special rubber that enables tires to maintain a pliable grip without stiffening even at temperatures lower than 7 degrees celsius.
Winter tires are divided largely into two types: studded and studless.

Studded Snow Tire
Studded winter tires have metal pins embedded in the tire surface to improve traction and braking force on icy and snowy roads. It is important to ensure that the studs do not affect the tread design and that they are protruded and spaced evenly.

Studless Snow Tire
While studded tires show excellent performance on icy and snowy roads, they cause damage to road surfaces. Studless tires are designed to have the highest traction capability possible on snowy or icy roads without stud pins.
All Season Tire

All-season tires have more tread kerfs than summer tires and are intended to be used year-round in regions with a short period of snow.
Summer Tire

Summer tires are used widely in all seasons except winter. Low noise, high ride quality and steering stability are the top priorities for these tires. Summer tires are synonymous with regular tires unless otherwise noted.
Tip for understanding!
What are “kerfs?”
Kerfs are thin slits or grooves cut in the tread block. They
are formed by side blades affixed to the tire curing mold.
Kerfs are cut into the tread blocks in order to improve
braking force and anti-side slip capability.
Bias Tire
Bias tires are used primarily for off-the-road, agricultural, and industrial vehicles.


Structure of a bias tire
The carcass of a bias tire has cords that alternate with one ply each in a crisscross angle formation. Thus, the angle of the alternating cords against the road surface is approximately 40 degrees on the circumference. Both carcass and belts are made out of nylon.
Change in tire tread while driving
Tread movement is sensitive to shifting weight and number of revolutions as treads wear down more quickly at high levels of heat. However, because the tread is fully capable of supporting weight, bias tires are appropriate for driving on unpaved roads and large vehicles. Their biggest advantage is flexibility and good drivability.
Radial Tire
Radial tires are produced for passenger cars, light trucks, trucks, and buses.


Structure of a radial tire
The radial tire refers to a tire in which the cords are arranged perpendicular to its circumference. Due to this cord arrangement, the radial tire has a lower flatness ratio than the bias tire. Also due to its high horizontal resistance, the radial tire has superior starting, acceleration, controllability, rotationality and safety characteristics and is best suited for high-speed travel. Both carcass and belts are made out of steel.
Change in tire tread while driving
Despite changes in radial tire tread while driving, you will notice no change in the contact area between tread and road surface. The radial tire is often used for passenger cars. Its advantages are high tread resistance and resistance to slipping while cornering due to low rolling resistance while driving.

Passenger Car Tires

Light Truck Tires

Truck & Bus Tires

Competition Car Tires

Agricultural Tires

Offroad Tires

Industrial Tires

Motorcycle Tires

Aircraft Tires
The Tire Labeling Regulation is an EU standard which offers helpful information for customers look to purchase our tires enabling them to check the tires characteristics before making a purchase. With eco-friendly products that are energy efficient and boast outstanding performance, Hankook is achieving its goal of satisfying customers and protecting the environment.
Aside from information on the label customers can also evaluate our excellent performance results by consulting charts and graphs which detail the running performance and numerous tests conducted by automobile magazines.
* You can also reduce fuel costs by using our eco-friendly tires. Please note that fuel expenses may differ depending on the make of vehicle, road condition and driving habits.
Hankook is working hard to provide useful information to customers in adopting the tire labeling regulation.
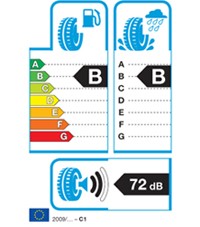
Regulations require tire manufacturers to declare fuel efficiency, wet grip rating and external rolling noise performance for C1, C2 and C3 tires (i.e. tires mainly fitted on passenger cars, and on light and heavy duty vehicles).
Lack of reliable and comparable information on the performance of tires currently makes it difficult for consumers to take these elements into account in their purchasing decision, especially when replacing a used set of tires. From 1st November 2012 tire performances data will be displayed at the point of sale and on all technical promotional literature such as catalogues, leaflets and web-based marketing.
The aim is to lead a market transformation towards a more fuel-efficient, safe and low-noise tire, beyond the standards already achieved. It will also pave the way for competition to run on tire performance and price, which will in turn stimulate investment in research and development.
(Source: European Commission)
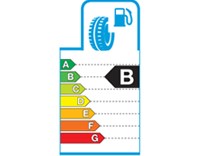
Fuel efficiency is measured by the rolling resistance (RR) of tires.
Rolling resistance is the resistance that occurs when a round object such as a ball or tire rolls on a flat surface in a steady velocity straight-line motion. It is caused mainly by the deformation of the object, the deformation of the surface, or both.
Additional contributing factors include wheel radius, forward speed, surface adhesion, and relative micro-sliding between the surfaces of contact. It depends very much on the material of the wheel or tire and the sort of ground.
| Class | PCR (C1) | LTR (C2) | TBR (C3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | RRC ≤ 6.5 | RRC ≤ 5.5 | RRC ≤ 4.0 |
| B | 6.6 ≤ RRC ≤ 7.7 | 5.6 ≤ RRC ≤ 6.7 | 4.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 5.0 |
| C | 7.8 ≤ RRC ≤ 9.0 | 6.8 ≤ RRC ≤ 8.0 | 5.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 6.0 |
| D | Empty | Empty | 6.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 7.0 |
| E | 9.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 10.5 | 8.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 9.2 | 7.1 ≤ RRC ≤ 8.0 |
| F | 10.6 ≤ RRC ≤ 12.0 | 9.3 ≤ RRC ≤ 10.5 | 8.1 ≤ RRC |
| G | 12.1 ≤ RRC | 10.6 ≤ RRC | Empty |
Seven classes from G (least efficient) to A (most efficient)
Effects may vary among vehicles and driving conditions, but the difference between a G and an A class for a complete set of tires could reduce fuel consumption by up to 7.5% and even more in the case of trucks.
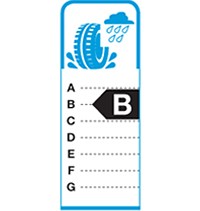
Wet grip indicates the braking performance of tires on wet road surfaces and is related to the safety performance of vehicles. Tires with low rolling resistance have high fuel efficiency, but can have safety problems. This is because tires with low rolling resistance have low adherence to roads when the roads are wet. Accordingly, the European Council requires tire companies to provide information about their tires adherence (or grip) when applying the brakes on wet roads.

| Class | PCR (C1) | LTR (C2) | TBR (C3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.55 ≤ G | 1.40 ≤ G | 1.25 ≤ G |
| B | 1.40 ≤ G ≤ 1.54 | 1.25 ≤ G ≤ 1.39 | 1.10 ≤ G ≤ 1.24 |
| C | 1.25 ≤ G ≤ 1.39 | 1.10 ≤ G ≤ 1.24 | 0.95 ≤ G ≤ 1.09 |
| D | Empty | Empty | 0.80 ≤ G ≤ 0.94 |
| E | 1.10 ≤ G ≤ 1.24 | 0.95 ≤ G ≤ 1.09 | 0.65 ≤ G ≤ 0.79 |
| F | G ≤ 1.09 | G ≤ 0.94 | G ≤ 0.64 |
| G | Empty | Empty | Empty |
Seven classes from G (longest braking distances) to A (shortest braking distances)
Effects may vary among vehicles and driving conditions, but in the case of full braking, the difference between a G and an A class for a set of four identical tires could be up to 30% shorter braking distance (e.g. for a typical passenger car driving at 80 km/h speed this could be up to 18m shorter braking distance).

Exterior noise levels are measured in decibel (dB) and are indicated in three categories (refer to the black bars on the left). The more black bars present, the more road noise is created from the tires.

In addition to the specification of noise level in Decibels (dB(A)) a pictogram displays whether the tire external rolling noise performance is above the future European mandatory limit value (three black bars = noisier tire), up to 3 dB below the future limit value (two black bars = average noise level) or more than 3 dB below the future limit value (one black bar = low noise tire).